Economic and mathematical problems, the purpose of which is to find the best (optimal) from the point of view of some criterion or criteria for the use of available resources (labor, capital, etc.), are called optimization.
Optimization problems (OZ) are solved using optimization models (OM) by methods of mathematical programming.
The structure of the optimization model consists of an objective function, a domain of permissible solutions, and a system of constraints that define that domain. The objective function in its most general form, in turn , also consists of three elements:
Managed variables Unmanaged variables the form of the function (the kind of dependency between them).
The scope of valid solutions is the area within which the choice of solutions is made. In economic problems, it is limited by available resources, conditions that are written in the form of a system of constraints consisting of equations and inequalities.
If the constraint system is incompatible, the scope of valid solutions is empty. Restrictions are divided into:
a) linear (I and II) and nonlinear (III and IV) (Figure 3.1.);
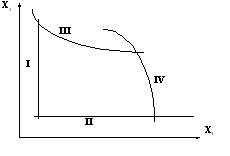
Fig.3.1. Linear and nonlinear constraints
b) deterministic (A, B) and stochastic (groups of curves ![]() ) (Fig.3.2.).
) (Fig.3.2.).

Rice. 3.2. Deterministic and stochastic constraints
Stochastic constraints are possible, probabilistic, random.
Optimization problems are solved by methods of mathematical programming, which are divided into:
linear programming; nonlinear programming; dynamic programming; integer programming; convex programming; operations research; geometric programming, etc.
The main task of mathematical programming is to find the extremum of functions with constraints in the form of equations and inequalities.
Consider the optimization problems solved by linear programming methods.
Optimization problems with linear dependence between variables
Let:
![]() – the amount of resource of the form i (i= 1.2,…,m);
– the amount of resource of the form i (i= 1.2,…,m);
![]() – the rate of consumption of i – th resource per unit j – th of the type of product;
– the rate of consumption of i – th resource per unit j – th of the type of product;
![]() – quantity of products of type j (j=1,2,…,n);
– quantity of products of type j (j=1,2,…,n);
![]() – profit (income) from a unit of this product (in the tasks for a minimum – the cost of production).
– profit (income) from a unit of this product (in the tasks for a minimum – the cost of production).
Then the optimization problems of linear programming (LP) in general form can be formulated and written as follows:
Find variables ![]() under which the objective function
under which the objective function
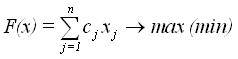 ,
,
would be the maximum (minimum) without violating the following restrictions:
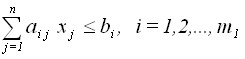 ,
,
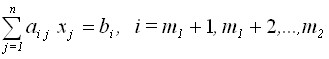 ,
,
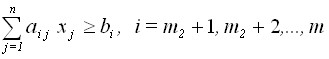 .
.
All three cases can be brought to the so-called canonical form by introducing additional variables:
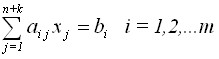 ,
,
k is the number of additional variables, and the non-negative condition of the desired variables:
![]() .
.
As a result of solving the problem, there is a certain plan (program) for the work of a certain enterprise. Hence the word “programming”. The word linear indicates the linear nature of the dependence both in the objective function and in the system of constraints. It should be emphasized once again that the task is necessarily extreme, i.e. consists in finding the maximum or minimum (extremum) of the objective function.