National wealth is one of the most important indicators of the country’s economic development, which represents the monetary expression of the totality of use values accumulated by society throughout its history as of a certain date.
For the first time, national wealth was calculated by the English economist W. Petty in 1664, in France it was calculated in 1789, in the USA – in 1803 and in Russia – in 1864.
In the modern economic literature, a unified approach to determining the structure of national wealth has not developed. Some economists include the entire stock of material goods created by labor and used for production and consumption. At the same time, natural wealth and labor are the sources and conditions for the creation of national wealth. Other scientists introduce natural resources as an element of national wealth. Still others believe that that national wealth can also contain intangible values – knowledge, information, culture, etc.
To calculate national wealth in accordance with the recommendations of the UN statistical service, the concepts of “assets” and “liabilities” are used.
Assets are property in respect of which institutional units exercise their ownership rights and from the possession and use of which they derive economic benefit. Assets include buildings, machinery and equipment, land, shares, bonds, deposits, etc. Each of them gives the owner a certain economic effect, benefit. Thus, buildings and structures create the necessary conditions for production activities. The use of more advanced machinery and equipment makes it possible to obtain an economic effect from the growth of labor productivity. Owners of cash deposits, shares and bonds receive income in the form of dividends and interest.
Liabilities are debts or obligations to pay off their debts. Liabilities are a source of formation of assets of economic entities. Typically, assets and liabilities are equivalent to each other.
Property is reflected in assets in value terms. This makes it possible to determine the total value of all property of a certain institutional unit. The total amount of assets minus liabilities (debt) forms equity. At the level of the national economy, the concept of “equity” corresponds to net assets, which characterize the size of the national wealth of the country.
What is included in the net assets of the economy? They are formed from tangible and intangible resources. Tangible assets include reproducible and unproductive assets (Table. 3.1.). The former are the result of labour for the entire period of its existence, the latter do not meet these requirements, but are necessary for the implementation of the production process. Thus, tangible assets as products of human activity include fixed assets, working capital, material and artistic values.
Fixed assets include durable goods used in the production process – buildings, structures, structures, machinery, equipment, etc. Working capital includes raw materials, materials, fuel, energy, semi-finished products, work in progress, etc. Values are goods of significant value that are not used in the sphere of production or consumption, but are stored for a long period of time as savings. These include precious metals, jewelry, paintings, etc. In addition to these elements, the composition of tangible assets includes funds that are not the results of production.
Table 3.1.
Structure of national wealth
Material assets | Reproducible | Fixed assets, working capital |
Non-reproducible | Land, natural resources | |
Intangible assets | Financial | Currency, securities |
Other intangible assets | Patents, copyrights |
However, property rights can be exercised in respect of them and they can be used in human activities. We are talking about land and its subsoil, i.e. natural resources included in production. Land in the System of National Accounts (SNA) is considered as a piece of land, including vegetation on it, as well as inland water bodies.
Under intangible assets in the SNA understand the rights that allow their owners to engage in certain types of activities, in particular the development of deposits, replication of products, etc. Formally, these rights take the form of patents, trademarks, copyrights, books, musical works, etc. The main element of intangible assets is financial, i.e. those objects that bring profit. Gold, securities, loans, cash, deposits, etc. can be allocated here.
National wealth is calculated on the basis of balance sheets. They are compiled at the beginning and end of a certain period in the form of tables that reflect the element-by-element composition of assets, liabilities and equity. There are three types of balances:
– initial balance sheet of assets and liabilities;
– changes in the balance sheet of assets and liabilities;
– Final balance of assets and liabilities.
The initial and final balance sheets are tables that reflect the value of assets, liabilities (liabilities) and equity at a certain point in time. Changes in the balance sheet are reflected in a table for statistical analysis of changes in equity.
The amount of national wealth is calculated as the total difference between assets and liabilities in all sectors of the economy (net assets) at the end of a certain period.
Currently, preparatory work is being carried out to calculate the national wealth of the Republic of Belarus according to the UN methodology. In the meantime, the national wealth of our country is calculated in accordance with the current methodology and its structure consists of fixed assets, material working capital and household property of the population. Thus, as of January 1, 2000, the national wealth amounted to (excluding denomination) 32116.9 trillion rubles. rubles, including the main production and non-production assets amounted to 28763.5 trillion rubles. rubles (or 89.6%), fig. 3.3.
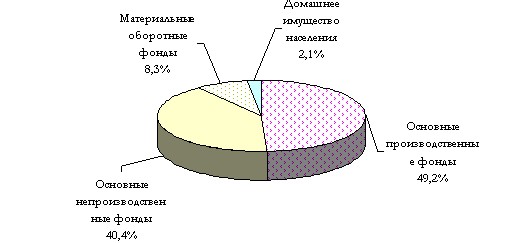
Rice. 3.3. The structure of the national wealth of the Republic of Belarus as of January 1, 2000 (excluding the value of land, subsoil and forests)
As social production develops, national wealth grows. The factors of its growth are:
– development and increase of national production;
– Wider and more diverse involvement of natural resources in economic use;
– introduction of achievements of scientific and technological progress and production experience;
– improving the educational and qualification level of employees;
– innovation and investment activity of business entities.
It should be noted that an increase in national wealth is a necessary condition for raising the standard of living of the people, a prerequisite and result of economic progress, the most important indicator of the economic power of the country.