To obtain information on the availability of certain groups of fixed assets, their technical condition and cost, fixed assets are accounted for both in kind and in value terms.
Fixed asset accounting data in physical terms make it possible to determine the production capacity of the enterprise, productivity, service life, composition, etc.
Monetary expression is necessary to determine the total value, structure and dynamics of fixed assets, calculate annual depreciation deductions, production costs, profitability of enterprises, real estate tax, etc. Since fixed assets are used for a long time, during which they gradually depreciate and change the conditions of reproduction, there are four methods of their monetary valuation: at original cost, replacement, residual and average annual.
The initial cost is the actual cost of creating fixed assets. It includes the costs of construction, manufacture or acquisition of fixed assets, delivery and construction and installation work. Thus, the initial cost of equipment is determined by the expression:
FP = C + Z + Zcm,
where: Ц – selling price of equipment, rub.;
3 – transportation costs for the delivery of equipment from the manufacturer to the installation site, rubles;
Zcm – the cost of construction and installation work at the place of operation of the equipment (foundation, installation, adjustment, etc.), rubles.
Valuation at historical cost is made in the prices of those years when fixed assets were created. At the initial cost, fixed assets are accounted for on the balance sheet of enterprises, so it is called book value. This method of valuation does not characterize the depreciation of fixed assets, does not allow to analyze their dynamics, does not show the actual value of funds at a given time.
Replacement cost is the cost of reproduction of fixed assets. It is determined by revaluation of fixed assets in the prices in force in the year when the revaluation is carried out. Replacement cost provides a unified estimate of fixed assets produced in different years. This allows you to establish the total amount of fixed assets, clarify their structure, compare fixed assets of enterprises and industries. All fixed assets listed on the balance sheet, regardless of their technical condition, except for the value of land plots and library funds, are subject to revaluation.
The replacement cost of fixed assets is determined by three methods.
1. By directly converting the value of objects into prices formed on a certain date for new objects, similar to those estimated and documented.
2. Using the index method based on the application of coefficients that take into account the increase in the cost of fixed assets at present compared to the date of commissioning. Conversion rates are developed by the Ministry of Statistics and Analysis for a certain date. With this method of recalculation, the replacement cost for groups of fixed assets is determined by the product of the original cost by the conversion factor, the value of which is determined according to the date of their commissioning.
3. Recalculation of the value of fixed assets manufactured abroad, purchased for foreign currency, at the exchange rate of the National Bank of the Republic of Belarus on the date of revaluation. At the same time, the cost of fixed assets in foreign currency is determined taking into account the contract price, customs clearance costs, delivery costs, etc.
The replacement cost does not reflect depreciation of fixed assets, so the valuation of fixed assets at residual value is applied.
Residual value is the initial (or replacement) value of fixed assets minus depreciation. Residual value (Fost) characterizes the unamortized part of the value of fixed assets, i.e. the value that has not yet been transferred to the finished products.
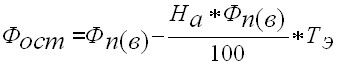
where: Na – depreciation rate, %;
Te – period of operation of fixed assets, years.
This method of evaluation is used in the sale of fixed assets that have been in operation, as well as in justifying the feasibility of replacing fixed assets.
Since the composition and structure of fixed assets changes with their arrival and disposal, there is a need to determine the average annual value of fixed assets.
The average annual cost (FSG) is determined on the basis of the cost of fixed assets at the beginning of the year (FNG), their planned input (Fvn) and disposal (FVIB) for the accounting period:
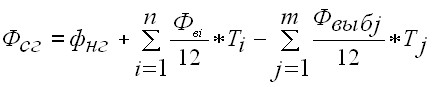
where: Ti – the number of full months from the date of introduction of fixed assets until the end of the year;
Tj – the number of full months from the date of disposal of fixed assets until the end of the year;
n – number of inputs of fixed assets;
m is the number of pins.
The average annual cost is used to calculate depreciation deductions for groups of fixed assets and general indicators of the effectiveness of their use.